مُصنِّع عجلات الطحن
بفضل أسعار الجملة المباشرة من المصنع، فإننا نتفوق كشركة مصنعة لأقراص الطحن - مورد أقراص الطحن المفضل لديك للحصول على منتجات عالية الجودة وخدمة استثنائية.
تُستخدم عجلات التجليخ لإزالة المواد، وتجليخ اللحام، وتجهيز الأسطح في تصنيع المعادن والصيانة الصناعية. وبالمقارنة مع عجلات القطع، صُممت عجلات التجليخ لتحمل الضغط الجانبي المستمر والتلامس الدائم مع قطعة العمل.
هذه الصفحة مخصصة للمشترين الصناعيين والموزعين وورش التصنيع الذين يختارون عجلات التجليخ للاستخدام المتكرر في الإنتاج. يتم عرض أنواع العجلات الشائعة بناءً على نوع المادة وزاوية التجليخ وشدة الحمل، مع التركيز على استقرار عملية القطع والتحكم في الحرارة والأداء المتسق عبر دفعات الإنتاج.
الشهادات
نوفر تشكيلة شاملة من عجلات الطحن المصممة لإزالة المواد بكفاءة في مختلف التطبيقات. تخضع كل عجلة لفحص جودة صارم، وهي مصممة للتوافق مع جميع آلات الطحن الزاوية القياسية، مما يضمن أداءً موثوقًا ومتانة طويلة الأمد في البيئات الصناعية الصعبة. عجلات الطحن لدينا معتمدة من MPA-ألمانيا، أعلى شهادة دولية للمنتجات الكاشطة، مما يدل على التزامنا بالسلامة والأداء والجودة.
ما هي وظيفة عجلات التجليخ؟
عجلات التجليخ هي أدوات كاشطة ملتصقة تُستخدم لإزالة المواد وتشكيل الأسطح وتجهيز الحواف. وعلى عكس عجلات القطع المصممة للقطع المستقيم، فإن عجلات التجليخ مصممة لتحمل التلامس المستمر والضغط الجانبي العالي والاحتكاك المتواصل.
في مجال تصنيع المعادن والصيانة الصناعية، تُستخدم عجلات التجليخ في تحضير اللحام، وتنظيف الأسطح، وإزالة النتوءات، وتشكيل الحواف، وإزالة العيوب. ويؤثر أداؤها بشكل مباشر على كفاءة التجليخ، وجودة السطح، والتحكم في الأدوات، وسلامة المشغل.
من الناحية التصنيعية، تُعدّ عجلات التجليخ أكثر تطلباً من الناحية الميكانيكية من عجلات القطع. إذ يجب أن تحافظ على سلامتها الهيكلية تحت تأثير الأحمال الجانبية مع ضمان إزالة المواد بشكل مُتحكّم به. وهذا ما يجعل اختيار المواد الكاشطة، وتركيبة المادة الرابطة، وتصميم التعزيز، والتحكم في عملية التصلب أموراً بالغة الأهمية.
تشرح هذه الصفحة كيفية صنع عجلات التجليخ، وكيف تتصرف التصاميم المختلفة في ظروف العمل الحقيقية، وكيفية اختيار عجلة التجليخ الصحيحة بناءً على التطبيق وبيئة التشغيل.

أنواع شائعة من عجلات التجليخ المستخدمة في تشكيل المعادن
عجلات تجليخ ذات مركز منخفض
تُعدّ أقراص التجليخ ذات المركز المنخفض، والمعروفة باسم النوع 27، من أكثر أقراص التجليخ استخدامًا في جلاخات الزوايا. يسمح مركزها المنخفض باستخدامها بزاوية ضحلة، مما يجعلها مناسبة لتجليخ الأسطح وإزالة اللحام.
تُستخدم عادةً للأغراض التالية:
-
طحن خط اللحام
-
تجهيز الحواف
-
تسوية السطح
-
إزالة الصدأ والطلاء
يوفر تصميمها توازناً بين سهولة الوصول والاستقرار، خاصة في أعمال التصنيع والبناء.
عجلات تجليخ مسطحة
تُستخدم عجلات التجليخ المسطحة عندما يكون التلامس الكامل مع السطح مطلوبًا. وهي أكثر شيوعًا في آلات التجليخ الثابتة أو المعدات المتخصصة، ويتم اختيارها لإزالة المواد بشكل متحكم فيه ومتساوٍ.
عجلات تجليخ رقيقة بسمك حوالي 6 مم
تُستخدم عجلات التجليخ التي يبلغ سمكها حوالي 6 مم غالبًا كحل وسط بين القطع والتجليخ. فهي تسمح بالتجليخ الخفيف مع توفير تحكم أفضل من العجلات الأكثر سمكًا.
عملياً، يتم اختيار هذه العجلات عندما:
-
المساحة محدودة
-
يرغب المشغلون في مزيد من الدقة
-
لا يلزم إزالة كميات كبيرة من المواد
ومع ذلك، فإن استخدامها لا يزال يتطلب تقنية صحيحة لتجنب الضغط الجانبي المفرط.
المواد الكاشطة وسلوك الطحن
أكسيد الألومنيوم وأكسيد الألومنيوم الأبيض
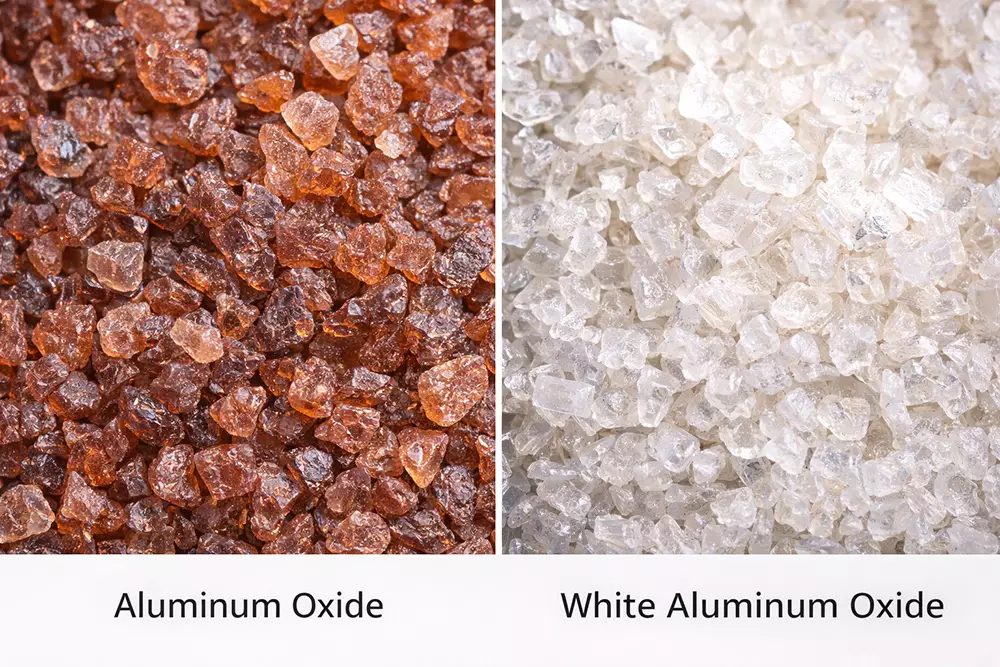

يُعد أكسيد الألومنيوم أكثر المواد الكاشطة استخداماً في طحن الفولاذ الكربوني. فهو يوفر أداءً مستقراً، وتآكلاً يمكن التنبؤ به، وكفاءة اقتصادية جيدة.
يتميز أكسيد الألومنيوم الأبيض بنقاوة أعلى ويتفكك بسهولة أكبر أثناء عملية الطحن. هذه الخاصية ذاتية الشحذ تقلل من تراكم الحرارة، مما يجعله مناسبًا للفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ والتطبيقات الحساسة للحرارة.
في الاستخدام الفعلي، توفر عجلات الطحن المصنوعة من أكسيد الألومنيوم الأبيض في كثير من الأحيان عملية طحن أكثر سلاسة ولكنها قد تتآكل بشكل أسرع إذا تم تطبيقها بضغط مفرط.
مواد كاشطة من الزركونيا والألومينا

تتميز مواد الزركونيا الكاشطة بصلابة ومقاومة للصدمات أعلى من أكسيد الألومنيوم القياسي. وغالبًا ما يتم اختيارها لعمليات التجليخ الشاقة التي تتطلب ضغطًا مستمرًا.
مع ذلك، يُظهر الزركونيا أفضل أداء له عندما يكون ضغط الطحن كافيًا لتفعيل آلية الشحذ الذاتي. في عمليات الطحن الخفيفة أو التطبيقات عالية السرعة ومنخفضة الضغط، قد لا يُظهر الزركونيا كامل مزاياه.
هذا سوء فهم شائع في السوق، حيث يتم الترويج للزركونيا أحيانًا على أنها متفوقة عالميًا بغض النظر عن التطبيق.
المواد الكاشطة الخزفية في عجلات التجليخ

توفر المواد الكاشطة الخزفية قطعًا قويًا وعمرًا طويلًا في التطبيقات الصعبة. وهي تُستخدم في عجلات التجليخ عالية الأداء المصممة لبيئات الإنتاج الصناعية.
يتطلب استخدامها تركيبة رابطة دقيقة وتصنيعًا مضبوطًا. وبدون توازن مناسب للرابطة، قد تبدو المواد الكاشطة الخزفية شديدة الخشونة أو غير مستقرة عند استخدامها يدويًا.
أنظمة الربط وصلابة العجلات
تعتمد عجلات التجليخ على أنظمة ربط راتنجية توازن بين الصلابة والمرونة. يجب أن تكون الرابطة قوية بما يكفي لحمل حبيبات الكشط تحت الضغط، ومرنة بما يكفي لتحرير الحبيبات الباهتة وكشف حواف قطع جديدة.
لا تُعدّ صلابة عجلة التجليخ مؤشراً بسيطاً على قوتها. فالعجلة الأكثر صلابة لا تدوم بالضرورة لفترة أطول. في العديد من تطبيقات التجليخ، تسمح الرابطة الأقل صلابة بتحسين عملية الشحذ الذاتي وتقليل توليد الحرارة.
في مجال التصنيع، يتم تعديل تركيبة الرابطة بناءً على:
-
نوع الكاشطة
-
سمك العجلة
-
الاستخدام المقصود
-
توقعات السوق المستهدف
يؤثر هذا التوازن بشكل كبير على ملمس الطحن وعمر الخدمة.
هيكل التعزيز واعتبارات السلامة
تُدعّم عجلات التجليخ بشبكة من الألياف الزجاجية لتحمّل الضغط الجانبي وقوى الدوران. ومن الهياكل الشائعة الاستخدام تقوية متعددة الطبقات من الألياف الزجاجية، والتي غالبًا ما تُرتّب على شكل تكوين ساندوتش 2+1.
هذا التعزيز يحسن ما يلي:
-
مقاومة التحميل الجانبي
-
الاستقرار الهيكلي أثناء الطحن
-
السلامة عند سرعات دوران عالية
يُعد عدم كفاية التعزيز أحد أكثر الأسباب شيوعًا لفشل عجلة التجليخ، خاصة عند استخدام العجلات بقوة أو بزوايا غير مناسبة.
عمليات التصنيع والخبرة العملية
طرق الضغط والتحكم في الكثافة
يمكن إنتاج عجلات التجليخ باستخدام الضغط البارد، أو الضغط شبه الساخن، أو الضغط الساخن. وتؤثر كل طريقة على الكثافة الداخلية وتوزيع الروابط.
يُعدّ الكبس على البارد فعالاً وشائع الاستخدام، ولكن في عجلات التجليخ السميكة، قد يؤدي عدم انتظام الكثافة إلى عدم اتساق عملية التجليخ. ولذلك، يُستخدم الكبس شبه الساخن أو الساخن لتحسين تجانس الكثافة وقوة الحواف.
من الناحية العملية، يتم تحديد طريقة الضغط بناءً على سمك العجلة وحمل الطحن المتوقع، وليس بناءً على سرعة الإنتاج وحدها.
المعالجة وتثبيت الروابط
بعد الضغط، تخضع عجلات التجليخ لعملية معالجة مضبوطة لتثبيت رابطة الراتنج. تضمن المعالجة الصحيحة ما يلي:
-
صلابة متناسقة
-
سلوك طحن مستقر
-
مقاومة التدهور الحراري
يؤدي عدم كفاية المعالجة إلى عجلات لينة تتآكل بسرعة، بينما قد تؤدي المعالجة الزائدة إلى عجلات هشة وعرضة للتشقق. ويتحقق هذا التوازن من خلال نطاقات معالجة معتمدة بناءً على نظام الراتنج وهندسة العجلة.
مراقبة الجودة في إنتاج عجلات التجليخ
يقوم المصنعون المحترفون بتطبيق العديد من فحوصات الجودة، بما في ذلك:
-
الفحص البُعدي
-
الفحص البصري
-
اختبار السرعة والتحمل
-
فحوصات التوازن للعجلات الأكبر حجماً
تُعد هذه الضوابط ضرورية لضمان السلامة واتساق الأداء، وخاصة بالنسبة لأسواق التصدير ذات ظروف التشغيل المتغيرة.
كيف تؤثر طريقة الضغط على ثبات عجلة الطحن؟
تختلف عجلات التجليخ اختلافًا كبيرًا عن عجلات القطع في الاستخدام الفعلي. فخلال عملية التجليخ، تتعرض العجلة لحمل جانبي ثابت وتلامس مستمر مع قطعة العمل. وهذا يعني أن الكثافة الداخلية وتوزيع الترابط يؤثران على الثبات بشكل أكبر بكثير مما هو عليه الحال في تطبيقات القطع.
في إنتاجنا، تعلمنا مبكراً أن استخدام الضغط البارد وحده لمواصفات معينة لعجلات التجليخ غالباً ما يؤدي إلى مشاكل لا تظهر إلا أثناء عملية التجليخ الفعلية. قد تبدو العجلات طبيعية بعد المعالجة، ولكن بمجرد تعرضها للضغط، قد تبدأ بالاهتزاز، أو تتزجج بشكل غير متساوٍ، أو تتآكل حافتها بسرعة أكبر. ترتبط هذه المشاكل عادةً بعدم تجانس الكثافة الذي يصعب اكتشافه بالعين المجردة.
لهذا السبب، لا نعتمد طريقة ضغط واحدة على جميع عجلات التجليخ. ففي الأقطار والسماكات المحددة التي تتطلب استقرارًا أكبر، نستخدم الضغط شبه الساخن أو الساخن لتحسين تجانس الكثافة. وقد تم اختيار هذه الطريقة لتحسين التحكم في عملية التجليخ وتقليل مخاطر عدم الاستقرار أثناء التشغيل لفترات طويلة.
المفاضلات العملية في إنتاج عجلات التجليخ
في صناعة عجلات التجليخ، لا تؤدي الصلابة العالية أو سرعة الإنتاج بالضرورة إلى أداء أفضل. في الواقع، غالباً ما يؤدي المبالغة في أي من هذين العاملين إلى ظهور مشاكل جديدة في الاستخدام الفعلي.
قد تدوم عجلات التجليخ شديدة الصلابة لفترة أطول في الاختبارات المُحكمة، ولكنها في التشغيل اليومي تميل إلى توليد حرارة أكبر، وانخفاض كفاءة القطع، وزيادة جهد المُشغل. ومع مرور الوقت، يؤدي ذلك إلى انخفاض الإنتاجية وعدم اتساق نتائج السطح. وتكون هذه الآثار ملحوظة بشكل خاص في عمليات التجليخ المستمر أو في بيئات العمل ذات درجات الحرارة العالية.
استنادًا إلى ملاحظات من تطبيقات وأسواق تصدير مختلفة، نُعدّل قوة الربط وطرق الضغط للحفاظ على التوازن بين معدل التآكل، ودقة القطع، والاستقرار التشغيلي. لا تستند قراراتنا إلى بيانات المختبر وحدها، بل إلى أداء العجلة تحت الضغط والحرارة الفعليين، وفي ظل ظروف العمل الميدانية.
تطبيقات الطحن النموذجية في الاستخدام الفعلي
تُستخدم عجلات التجليخ في:
-
تصنيع الهياكل الفولاذية
-
التحضير والتشطيب للحام
-
أعمال البناء والبنية التحتية
-
صيانة المعدات
-
عمليات الإصلاح الصناعي
في المناطق ذات درجات الحرارة المرتفعة مثل جنوب شرق آسيا وأمريكا الجنوبية والشرق الأوسط، قد تؤدي دورات الطحن المطولة إلى زيادة الإجهاد الحراري على عجلات الطحن. في هذه الظروف، غالباً ما يكون استقرار الترابط وجودة التعزيز أكثر أهمية من درجة الكشط الاسمية.
متى لا يكون استخدام عجلة التجليخ هو الخيار المناسب
صُممت أقراص التجليخ لإزالة المواد تحت ضغط جانبي مُتحكم به، لكنها لا تُناسب جميع العمليات. عمليًا، تنشأ العديد من مشاكل الأداء والسلامة من استخدام قرص التجليخ في حالات يكون فيها استخدام أداة أخرى أكثر فعالية.
من الأخطاء الشائعة استخدام عجلة التجليخ للقطع المستقيم. فرغم أن العجلة قد تبدو قوية، إلا أنها غير مصممة لتحمل قوى القطع من الحافة. وهذا غالبًا ما يؤدي إلى ارتفاع درجة الحرارة بشكل مفرط، وتآكل سريع للحافة، وزيادة خطر تلف العجلة. وللقطع المستقيم، تُعد عجلة القطع الخيار الأمثل والأكثر أمانًا.
تظهر مشكلة أخرى عند استخدام عجلات التجليخ شديدة الصلابة على قطع العمل الرقيقة أو المرنة. في هذه الحالات، تميل العجلة إلى توليد حرارة أسرع من إزالة المادة. وقد يواجه المشغلون مشكلة التزجيج، وضعف استجابة القطع، والحاجة إلى تطبيق ضغط أكبر، مما يقلل من التحكم والاتساق.
لا تُعدّ أقراص التجليخ مناسبةً أيضاً لماكينات التجليخ الزاوية منخفضة الطاقة عند استخدام مواد كاشطة قوية أو مواد ذات روابط صلبة للغاية. في مثل هذه الحالات، لا يستطيع القرص شحذ نفسه بشكل صحيح. فبدلاً من القطع بكفاءة، يحتك بالسطح، مما يُنتج اهتزازاً وتآكلاً غير متساوٍ. غالباً ما يُفسَّر هذا خطأً على أنه مشكلة في الجودة، بينما السبب الحقيقي هو عدم التوافق بين تصميم القرص وظروف التشغيل.
في التطبيقات العملية، لا يؤدي اختيار قرص التجليخ الخاطئ عادةً إلى فشل فوري، بل تتراكم المشاكل تدريجيًا على شكل تراكم للحرارة، وعدم استقرار في التشغيل، وإرهاق المشغل. لهذا السبب، غالبًا ما يكون اختيار الأداة والمواصفات الصحيحة أكثر أهمية من اختيار القرص الأكثر صلابة أو متانة.
كيفية اختيار عجلة التجليخ المناسبة
ينبغي أن تبدأ عملية الاختيار بتقديم الطلب:
-
تُعدّ عملية طحن الفولاذ الكربوني فعالة بشكل عام مع أكسيد الألومنيوم.
-
يستفيد الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ من أكسيد الألومنيوم الأبيض أو تركيبات الزركونيا المحسّنة
يجب أن يتناسب سمك وقطر عجلة التجليخ مع الأداة وضغط التجليخ المطلوب. توفر العجلات الرقيقة تحكمًا أفضل، بينما توفر العجلات السميكة ثباتًا أكبر للتجليخ الثقيل.
يجب دائمًا التحقق من سرعة التشغيل وتوافق الجهاز لضمان الاستخدام الآمن.
| طلب | نوع المادة | عجلة التجليخ الموصى بها | فائدة |
|---|---|---|---|
| طحن خط اللحام | الفولاذ الكربوني والفولاذ منخفض السبائك | عجلات من أكسيد الألومنيوم من النوع 27 | اتصال ثابت، إزالة سريعة |
| تحضير السطح | الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ | عجلات من أكسيد الألومنيوم الأبيض | انخفاض تراكم الحرارة |
| الطحن الثقيل | حديد الزهر، سبيكة عالية | عجلات من الألومينا الزركونية | إزالة المخزون العالي |
مسؤولية التخصيص والتصنيع من قبل الشركة المصنعة الأصلية
يقدم مصنعو عجلات التجليخ المحترفون خيارات تخصيص للمصنعين الأصليين مثل:
-
تعديل تركيبة المواد الكاشطة
-
ضبط صلابة العجلات
-
تخصيص السماكة والقطر
-
خيارات حجم العريشة
-
تصميم الملصقات والتغليف
في الوقت نفسه، يلتزم المصنّعون المسؤولون بحدود فنية واضحة. وقد يتم رفض بعض تركيبات المعايير إذا كانت تُعرّض السلامة أو الأداء للخطر.
يُعد هذا التوازن بين المرونة والمسؤولية مؤشراً هاماً على جودة التصنيع.
معايير الصناعة والامتثال لها
تُصنع عجلات التجليخ وفقًا لمعايير السلامة المعترف بها، مثل معيار EN12413 للمواد الكاشطة المُلصقة. ويضمن هذا الالتزام الحد الأدنى من أداء السلامة في ظل ظروف التشغيل المُحددة.
ينبغي اعتبار الامتثال للمعايير شرطاً أساسياً وليس ميزة مميزة.
تُعدّ أقراص التجليخ أدوات هندسية يجب أن تُوازن بين قدرة القطع والمتانة والسلامة وسهولة تحكم المُشغّل. ويتحدد أداؤها في الاستخدام الفعلي بقرارات التصنيع التي تُتخذ قبل وصول القرص إلى المستخدم بفترة طويلة.
بالنسبة للمشترين والموزعين، يُتيح فهم هذه الأساسيات اختيار المنتجات وتقييم الموردين بشكل أكثر دقة. ولا يُحدد مورد عجلات التجليخ الموثوق به بمجرد الادعاءات المتعلقة بالمنتج، بل بجودة التصنيع المتسقة والمعرفة العملية بالتطبيقات.
خط خاص SG-PLUS (عجلات الطحن المقواة)
-
للصلب
- كاشط: أكسيد الألومنيوم أ
- صلابة: ر (صعب جدًا)
- التطبيقات: شطف اللحامات، إزالة النتوءات، طحن الأسطح الثقيلة
- سمات: أداء قطع متميز، وعمر أداة استثنائي، ومُحسَّن للاستخدام مع المطاحن الزاوية الهوائية والكهربائية عالية الطاقة
-
للحجر والحديد الزهر
- كاشط: كربيد السيليكون C
- صلابة: R (أداة احترافية متوسطة الصلابة)
- التطبيقات: قطع وطحن الحجر الطبيعي والصناعي والحجر المقاوم للحريق والحديد الزهر والألمنيوم الصلب
- سمات: ثبات جانبي عالي، عمر خدمة طويل، مناسب لآلات الطحن الزاوية وآلات الطحن عالية التردد

خط الأداء SG-ELASTIC (عجلات الطحن المقواة)
- كاشط: أكسيد الألومنيوم أ
- صلابة: س (أداة احترافية صلبة)
- مواد: الفولاذ والفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ (INOX)
- التطبيقات: طحن السطح على طبقات اللحام، شطف الحواف، إزالة النتوءات، طحن اللحامات، الحقن
- سمات: طحن قوي تحت الأحمال العالية، عمر طويل للأداة، امتصاص ممتاز للاهتزازات

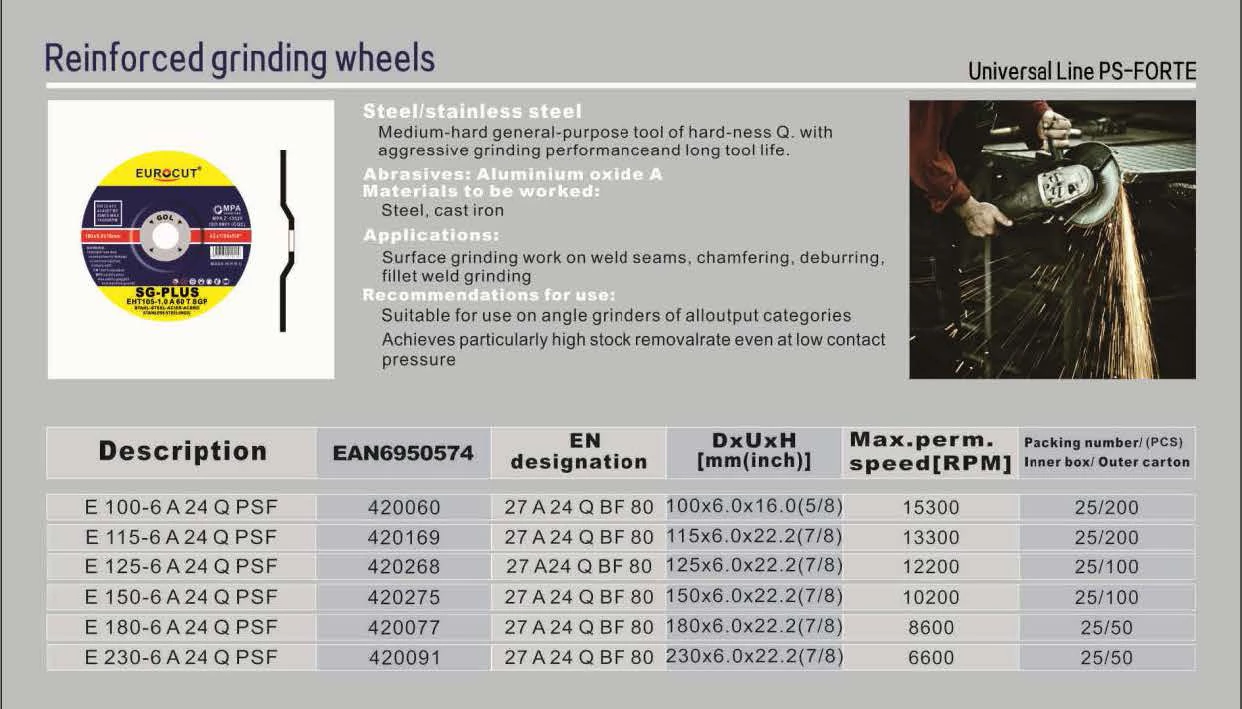
خط عالمي PS-FORTE (عجلات الطحن المقواة)
- كاشط: أكسيد الألومنيوم أ
- صلابة: Q (متوسطة الصلابة للأغراض العامة)
- مواد: الفولاذ والحديد الزهر
- التطبيقات: طحن السطح، شطف الحواف، إزالة النتوءات، تشطيب اللحام بالشرائح
- سمات: أداء قطع متوازن جيدًا، وعمر طويل، وإزالة عالية للمخزون حتى عند ضغط تلامس منخفض
لماذا تختارنا؟
-
تحسينات على المنتجات الموثوقة والمجربة، مما يزيد من كفاءة أدواتك.
-
طحن دقيق، مما يضمن سطحًا خاليًا من الخدوش على قطعة العمل الخاصة بك.
-
عمر أداة ممتد بشكل كبير، تم اختباره في التطبيقات الواقعية.
لماذا تثق في تشينغ يانغ
تشينغ يانغ هي علامتنا التجارية الخاصة التي طورناها بعناية، والمخصصة لتقديم مجموعة واسعة من منتجات الكاشطة عالية الأداء والجودة العالية والفعالة من حيث التكلفة. هذا ليس مجرد شعار، بل نحن نحمل شهادة MPA, أعلى مستوى من الشهادة لطحن المنتجات في جميع أنحاء العالم، وهو ما يعكس التزامنا القوي بالسلامة والأداء والاتساق.
كل أداة كاشطة من تشينغ يانغ تلبي المعايير الصارمة ايزو 9001 تخضع كل دفعة إنتاج لاختبارات صارمة لقوة الالتصاق، وثبات الحبيبات، ودقة الأبعاد، مما يضمن عملية تصنيع قابلة للتتبع ومراقبة جودة لا هوادة فيها.
منتجاتنا موثوقة ومفضلة لدى المشترين والمهندسين في أكثر من 50 دولة ومنطقة حول العالم. بالتعاون معنا، يمكنك الحصول على عجلات وأقراص طحن عالية الجودة، حاصلة على أعلى شهادات الجودة في هذا المجال.
اختيار عجلة التجليخ المناسبة لعملك
تؤثر صلابة عجلة التجليخ ونوع حبيباتها وسماكتها على الأداء تحت الحمل. تشرح هذه الأدلة كيفية مطابقة المواصفات مع ظروف التجليخ الفعلية لديك.
اختيار أقراص التجليخ لإزالة اللحام
نوع الحبيبات، وصلابة الترابط، وسمك القرص - مطابقة لملف تعريف اللحام والمادة.
عجلات التجليخ مقابل أقراص الصنفرة
التصميم الهيكلي، وسلوك التحميل، ومتى تنتمي كل أداة إلى تسلسل العملية.
لماذا تتعطل عجلات التجليخ قبل الأوان؟
أخطاء التطبيق مقابل عيوب التصنيع - تحليل الأسباب الجذرية لبيئات الإنتاج.
أحجام عجلات الطحن
| مم | بوصة | SPEEDR.PM | سبيد إم/إس | PCS/CTN |
| 100×4.0×16 | 4×1/8×5/8 بوصة | 15200 | 80 | 300 |
| 100×6.0×16 | 4×1/4×5/8 بوصة | 15200 | 80 | 200 |
| 115 × 6.0 × 22.2 | 4 1/2×1/4×7/8 بوصة | 13300 | 80 | 200 |
| 125 × 6.0 × 22.2 | 5×1/4×7/8 بوصة | 12200 | 80 | 100 |
| 150 × 6.0 × 22.2 | 6×1/4×7/8 بوصة | 10200 | 80 | 100 |
| 180 × 6.0 × 22.2 | 7×1/4×7/8 بوصة | 8500 | 80 | 50 |
| 230 × 6.0 × 22.2 | 9×1/4×7/8 بوصة | 6640 | 80 | 50 |
خدمات طحن العجلات المخصصة
الشركة المصنعة الشهيرة لعجلات الطحن تشينغ يانغ لا تنتج منتجات تحت علامتها التجارية فحسب، بل تقدم أيضًا منتجات شاملة حلول التخصيص OEM/ODM لعجلات الطحن. منتجاتنا المُخصصة تُلبي المتطلبات الأكثر إلحاحًا في صناعة الطحن العالمية، بشهادات تصل إلى أعلى المستويات. شهادة MPA مستوى.
تخصيص الحجم المرن
نحن نقدم مواصفات حجم مرنة للغاية:
-
القطر الخارجي:تتوفر مجموعة واسعة من العجلات، من العجلات المدمجة مقاس 3 بوصات إلى العجلات الكبيرة مقاس 9 بوصات شديدة التحمل، وكلها قابلة للتخصيص وفقًا لمتطلباتك.
-
القطر الداخلي:قابلة للتخصيص أيضًا (على سبيل المثال، الأحجام القياسية مثل 16 مم، 22.2 مم، 25.4 مم، أو أبعاد خاصة لتناسب معداتك).
-
سماكة:يتم التحكم فيه بدقة لتلبية متطلبات شدة الطحن المختلفة عبر التطبيقات المختلفة.
مواد وأداء مُحسَّن
يقوم فريق الهندسة لدينا بتصميم تركيبة المواد الكاشطة ونسب المواد الرابطة بناءً على تطبيقك المحدد - سواء كان ذلك معالجة المعادن أو معالجة الأحجار أو الطحن للأغراض العامة.
باستخدام التقنيات المتقدمة مثل المعالجة المضادة للكهرباء الساكنة والطلاءات المقاومة للحرارة، يمكن لعجلات الطحن المخصصة لدينا أن تتطابق مع أداء العلامات التجارية الرائدة في الصناعة مثل نورتون و كلينجسبور.
ابني علامتك التجارية الخاصة
هل ترغب في تأسيس علامتك التجارية الخاصة؟ نقدم لك خدمات التخصيص الشاملة، بما في ذلك:
-
طباعة الملصقات المخصصة
-
نظام تحديد الحصى المرمز بالألوان
-
بيانات المنتج الحصرية
نحن نغطي مجموعة واسعة من عجلات الطحن، بما في ذلك:
-
عجلات المطحنة الزاوية القياسية
-
عجلات طحن شديدة التحمل
سواءً بناءً على عيناتكم الحالية أو رسوماتكم الفنية، يُمكننا تصميم عجلات طحن مُصممة خصيصًا لكم. كما ندعم تكرار الإنتاج الضخم، وتحسين الأداء، واختبار جدوى العينات على دفعات صغيرة.
ضمان الجودة
يتم تصنيع جميع عجلات الطحن المخصصة بموجب نظام مراقبة الجودة الصارم ويتم اعتمادها في النهاية بواسطة MPA، ضمان الامتثال الكامل لمعايير السلامة والأداء الدولية.
 ابدأ مشروعك المخصص
ابدأ مشروعك المخصصما يقوله العملاء السعداء
- مدير تطوير الأعمال
الأسئلة الشائعة
أساسيات عجلة الطحن
س: ما هي عجلة الطحن؟
ج: عجلة الطحن (وتُسمى أيضًا قرص التلميع) هي أداة طحن على شكل قرص، مصنوعة من جزيئات كاشطة حادة مترابطة بمادة رابطة راتنجية. تستخدم شركة تشينغ يانغ تركيبات كاشطة متنوعة تناسب ظروف التشغيل المختلفة، وجميع منتجاتها متوافقة مع واجهات آلات الطحن الزاوية القياسية. تحتوي عجلة الطحن المقواة على طبقات متعددة من شبكة الألياف الزجاجية عالية القوة في طبقة الراتنج، مما يزيد من عمر الخدمة بمقدار 50% ويضمن ثبات الهيكل في ظروف العمل القاسية.
س: ما هي الاستخدامات الرئيسية لعجلات الطحن؟
أ: تشمل الوظائف الأساسية خمسة مجالات رئيسية:
- معالجة سطح المعدن (إزالة الصدأ/تنظيف ندبة اللحام)
- إزالة النتوءات الصناعية
- إصلاح الصفائح المعدنية للسيارات
- المعالجة المسبقة للركيزة الخرسانية
- إزالة المواد بسرعة (مثل قطع الهيكل الفولاذي)
تطبيق مبتكر:يمكن لقرص الطحن الهجين مقاس 1/8 بوصة (حوالي 3.2 مم) إكمال القطع والطحن الخشن في نفس الوقت، مما يقلل من وقت استبدال الأداة بنسبة 70% في عمليات قضبان الفولاذ/الأنابيب المعدنية.
النموذج والمعايير الفنية
س: ما هو الفرق بين عجلات الطحن T1 و T27؟
| نموذج | السمات الهيكلية | السيناريوهات القابلة للتطبيق |
|---|---|---|
| ت27 | المستوى المقعر المركزي | طحن الطائرة التقليدية |
| ت29 | تصميم محدب السطح المنحني | تشغيل بزاوية ≥45 درجة |
| ت1 | هيكل مزدوج الجوانب مسطح بالكامل | مخصص لقطع الأقراص/مطاحن المقاعد |
س: كيفية اختيار المواد الكاشطة؟
أ: الحلول الموصى بها بناءً على خصائص المعدن:
- أكسيد الألومنيوم: المعادن السوداء مثل الفولاذ الكربوني/الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ (مقاوم للتلبيد في درجات الحرارة العالية)
- صيغة مركب كربيد السيليكون: مخصص للمعادن اللينة مثل الألومنيوم/النحاس (تقنية مقاومة للانسداد حاصلة على براءة اختراع)
اختراق تقني:تتبنى عجلة الطحن المعدنية الناعمة Qing Yang عملية الطحن ذات درجة الحرارة المنخفضة، والتي يمكنها تقليل ارتفاع درجة حرارة قطعة العمل بواسطة 65% من خلال التحكم في مستشعر الضغط.
دليل التشغيل الآمن
س: هل يمكن استخدام عجلات الطحن وأقراص القطع معًا؟
ج: ممنوع منعًا باتًا! الفروق الجوهرية هي كما يلي:
| نوع الأداة | نطاق السُمك | التموضع الوظيفي | تحذير من المخاطر |
|---|---|---|---|
| عجلة الطحن | 1/4 بوصة (6.4 مم) | طحن السطح | قد تؤدي عملية القطع إلى الانفجار |
| قرص القطع | ≤3/32 بوصة (2.4 مم) | تقسيم المواد | قد يتفكك في طبقات أثناء الطحن |
للحصول على شرح كامل للاختلافات الهيكلية ولماذا يعتبر الاستبدال غير آمن:
س: ما هي القواعد الحديدية للتشغيل الآمن؟
أ: هناك 10 إرشادات رئيسية يجب اتباعها:
- حماية ثلاثية: قناع + قفازات مضادة للقطع + سدادات أذن عازلة للضوضاء
- فحص ما قبل البدء: يجب التخلص من عجلات الطحن المتشققة/المعيبة على الفور
- مطابقة الطاقة: الطاقة المقدرة لطاحونة الزاوية ≥ متطلبات عجلة الطحن
- تعطيل الغطاء الواقي: يُمنع منعًا باتًا إزالة أو تعديل الأجهزة الواقية
- التحكم في السرعة: سرعة عدم التحميل للمعدات ≤ علامة الخط الأحمر لعجلة الطحن
- مواصفات البدء والإيقاف: البدء في وضع الخمول لمدة 30 ثانية → التشغيل → التوقف الكامل قبل المغادرة
- وضعية التشغيل: الإمساك بكلتا اليدين + وضعية الوقوف المستقرة
- متطلبات الملابس: ملابس عمل ضيقة + ربطة شعر (لمنع التشابك)
- الصيانة الدورية: تحقق من حالة فرشاة الكربون للمحرك في كل وردية
- الاستعداد للطوارئ: تكوين معدات إطفاء الحرائق ضمن دائرة تشغيلية تبلغ 3 أمتار
انظر أيضًا: أنماط الأعطال الناتجة عن أخطاء التشغيل الشائعة:
دليل الشراء
س1: ما هي مدة الإنتاج؟
أ:
- الأحجام القياسية موجودة في المخزون ويمكن شحنها خلال 3 أيام.
- بالنسبة للمنتجات غير القياسية أو المخصصة، فإن مهلة الإنتاج تكون تقريبًا من 30 إلى 40 يومًا.
س2: هل أنتم مصنع أو شركة تجارية؟
أ: نحن شركة مصنعة محترفة للأدوات الكاشطة مع أكثر من 35 عامًا من الخبرة.
س3: هل تقبل العلامة التجارية OEM؟
أ: نعم، تتوفر خدمة تصميم العلامات التجارية الأصلية (OEM). كما نقدم خدمات تصميم الملصقات مجانًا.
س4: هل العينات متاحة لاختبار الجودة؟
أ: نعم، تتوفر عينات مجانية لاختبار الجودة. يتحمل العميل تكلفة الشحن.
س5: هل لديك أية شهادات؟
أ: نعم، نحن معتمدون وفقًا لمعايير MPA و ISO.
س6: ما هي مدة التسليم؟
أ: عادة، يستغرق التسليم حوالي 20 يومًا بعد استلام الدفع.
أدلة استخدام عجلة التجليخ
أدلة الاختيار، وتحليل الأعطال، وحدود السلامة - وكلها خاصة بتطبيقات عجلة الطحن في تصنيع المعادن.
الاختيار والتطبيق
اختر مواصفات العجلات بما يتناسب مع متطلبات إزالة المواد الخاصة بكاختيار أقراص التجليخ لإزالة اللحام
نوع الحبيبات، وصلابة الترابط، وسماكة القرص لطحن اللحام الثقيل.
→ مقارنةعجلات التجليخ مقابل أقراص الصنفرة
لماذا تعمل هذه الأدوات بالتتابع، وليس كبدائل؟.
→ تحليل الأعطاللماذا تتعطل عجلات التجليخ قبل الأوان؟
أخطاء التطبيق التي تتسبب في معظم حالات الفشل المبكر.
→حدود الأمان
أخطاء استبدال الأدوات التي تؤثر على عمليات عجلة التجليخأخطاء شائعة في اختيار أدوات الكشط
كيف يؤدي استخدام أقراص القطع في عمليات التجليخ وأخطاء اتجاه الحمل الأخرى إلى حدوث أعطال.
→ الحدودلماذا لا ينبغي استبدال عجلات التجليخ بأقراص الصنفرة؟
الأسباب الهيكلية التي تجعل أقراص الصنفرة تفقد كفاءتها تحت أحمال الطحن الثقيلة.
→ مقارنةأقراص القطع مقابل أقراص التجليخ
اتجاه الحمل، والتصميم الإنشائي، ولماذا لا يمكن استبدال أحدهما بالآخر.
→











